Smart fabric

In the future smart fabric, dresses will change colour and temperature, act as your smartphone screen and even create electric power – all this concentrated on sustainability. With improvement in modern technologies smart textiles fabrics are also improved to give value to the wearer.
What is a smart fabric?
The world is undoubtedly advancing towards the modern era, an era of bright and intelligent discoveries; problem-solving and creativity − the smart automobile vehicles (autos, metro system), intelligent planes, homes and amongst of multiple of such refined paradigms, the ‘Smart and Intelligent Textiles’.There is a substantive distinction between the words, ‘Smart’ and ‘Intelligent’, Smart materials or textiles can be described as the elements and structures which have the knowledge or can sense the environmental conditions or stimuli. In diversity, intelligent textiles can be characterised as textile structures which not only can recognise but can also take and respond to ecological requirements or stimuli. These stimuli, as well as an acknowledgement, could be thermal, biochemical, mechanical, electrical, magnetic or from a different source.
According to the mode of reaction, they can be classified into
passive smart
active smart
very smart
Passive smart fabric
Passive smart materials can sense the environmental circumstances or stimuli; they are sensors.
Active smart fabric
Active smart materials will sense and respond to the conditions or stimuli; besides the sensor function, they also have actuation characteristics.
Very smart
Very smart stuff can sense, respond and adapt themselves accordingly an even higher level of intelligence can be achieved from those original materials and structures capable of reacting or activated to execute a function in a standard or pre-programmed manner.
History
Its discovery in the 1960s by the American firm DuPont, the artificial fibre Lycra, or Spandex as it is identified in America, is one of the many commonly applied smart fabric and has been extensively utilised, due to its outstanding elasticity, in the sport and fashion business. The active thread is not restricted to Levi’s. Designers from all across the world have previously worked on fabrics that are not just green but able of shifting colours, regulating the body’s temperature and operating like a touchscreen. It will not take long for intelligent interactive fabrics to turn more available to the citizens. Besides sensors, these elements carry pre-programed activators that act in certain conditions. With thermic reaction, for example, by assuming that the environment is too sizzling, the fabric can initiate thermoregulators that do the weft thread to consume heat and give ideal temperature for the user.
WORKING
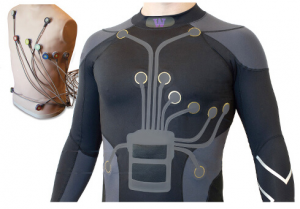
Heat and safety in cold Antarctica
Millions of workers throughout the world practice their jobs under intense conditions. One of these conditions is severe winter, which demands the usage of clothes that weigh up to ten kilos. In such incidents, the general health hazards, especially for injuries, stretch. Conscious of this, Qoowear, a US-based corporation, has developed a smart outfit that addresses the requirements of researchers in the Antarctic and Arctic and likewise exposed workers in the oil and gas, shipping, drilling, mining and construction sectors.
Electric or smart textiles
Electric either smart textiles, such as heat and light-sensitive goods, were developed initially as intelligent or smart clothes for the sportswear warehouse, and created fabrics for products that were designed to secure computing or digital segments.
Footwear
Footwear uses plasma as a thermal vector and operates Artificial Intelligence to identify in real-time the coldest spots of the body. With this report, the clothing stimulates plaques which heat up in strategic places of the body, such as the thorax, the stomach and the thigh, maintaining the temperature and checking the worker or researcher from cold and from disappointing to fulfil their duties.
Benefits
Smart textiles have the technology and knowledge to improve how healthcare providers associate with their patients. Smart clothes or e-textiles for healthcare can add weaving electronics into a report of clothing to make patient care functions. These textiles can authorise healthcare providers to have access to real-time patient data and even inform them of possible warning signs. Smart fabric would enable the patients to be monitored by healthcare providers as they go about their daily lives which can ultimately reduce the number of clinic visits for the patient. Some smart clothing involves gloves with sensors, socks that have tiny blood pressure sensors, and wearable intelligent commodities that can regulate stress. They can cooperate with both the environment and the user while transmitting real-time data about the user to another device. E-textiles are the eventuality of home-based fitness monitoring because they can accommodate a comfortable and secure environment for home healthcare and sickness prevention.
- Can identify early warning signs that indicate disease.
- Can be used in an expert medical setting or can be used to control personal health.
- Telemedicine- provides for a doctor to observe a patient without being with them
- GPS tracking in e-textiles can be applied to follow senior family members enduring from Dementia or Alzheimer’s
- Built-in displays that can give you information, pictures and video you would typically view on a PC or smartphone screen.
- Communication with a system using certain gestures by touching your clothing.Powerful, tiny sensors that monitor biological functions
Disadvantages
- Over notifying can overstimulate our senses.
- If vibration or lighting/colour variations are used to take our attention, this might be helpful if it is managed sparingly. If we get a much of buzzes on our skin, or our clothing quickly is changing colour or displays or lights are blinking at us too much, smart fabrics products could make people sick.
- Accidental interactions can cause unintended results.
- What if I can command my TV programs with my jeans by indicating on the fabric, but each time I change positions in my chair, I change the channel
- Controlling inputs, determining touch targets and gestures, as well as what to display, and how to notify people of events are challenging to implement well on something that is always touching your skin.
- We live in society, and smart fabrics might accidentally present personal information that we wouldn’t want others to view.
Read More E-textiles