Cyber security
What is Cyber Security?
cyber security is the practice of protecting malicious attacks on computers, servers, mobile devices, digital systems, networks, and information. It also is recognized as the security of information technology, or the security of electronic information. The word encompasses a number of contexts, from industry to mobile technology.
Figure 1. Cyber security
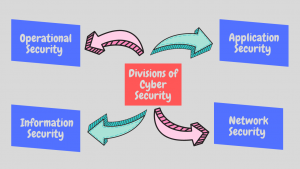
The different divisions of Cyber Security:
- The security of Network: Network protection is the process of protecting intruders from a computer network, be it focused on attackers or duplicitous malware.
- Security of application: Various kinds of security systems, including such proxy servers, antivirus programs, encryption programs as well as other tools, may help to avoid remote access. Organizations may also recognize and secure confidential data resources by unique application protection mechanisms that are connected to those data sets. Application protection is one of several levels of security employed by organizations to secure networks. See also security of the operating system, reliability of the data, and endpoint or safety of the smartphone.
- Information security: It is associated with data security from threats of any kind. Protection of information seeks toward unauthorized access, alteration of dissemination, and disruption. Experts in the area of information security are the basis of data incident management particular protocol with its prioritizing assets first before resolving attacks.
- Operational security: Operational safety, which is also a method of organizational protection, is a risk assessment mechanism that allows managers to assess activities from an adversary’s viewpoint to prevent sensitive information against getting into the wrong hands. Human beings are the weakest point of every organization’s operational security measures as they commit mistakes, miss specifics, neglect stuff, and circumvent stuff.
- Disaster recovery and business continuity: More than 75 percent of entrepreneurs say they have no disaster recovery plan. This data point is really quite shocking, particularly if you look at the millions of cyber-attacks on business owners every year. Several researchers have shown that about Forty percent of firms suffering a cyber-attack quickly shut their doors. Rather than preparing before a catastrophe occurs, now would be the time to focus on creating a strategy for business sustainability and recuperation of disasters. The easiest place to focus on what this program aims to accomplish is to partner with IT experts.
Figure 2. The different divisions of Cyber Security
What is a Cyber Threat?
A cyber or cyber security malicious code act that generally intends to harm data, steal information or interrupt digital life. Cyber attacks cover computer viruses, security breaches, Denial of Service (DoS) assaults, as well as other topology of attack. Cyber attacks also refer to the ability of an effective cyber attack aimed at gaining illegal entry, damage, disruption, or attempting to steal an IT investment, computer network, proprietary information, and any other establishment of confidential information. Cyber threats can come from authorized users in an organization or from unknown parties from remote locations.
The types of Cyber threats:
- Malware: Malicious software is the common term for many variants of malicious malware, such as viruses. Phonetic malicious generally consists of software written by attackers to inflict significant damage to information and services or to obtain unauthorized access to the network. Malicious software is usually distributed via email throughout the context of a connection or file and allows the user to follow the link or download a file for infection execution.
There are a variety of different forms of malware including:
- Virus: A computer virus is a computer program that reproduces and reflects the way a machine operates by transferring it to another application, device booting sector, or text. The virus needs anyone to transmit the disease consciously or unwittingly, without even a user and system administrator’s awareness or approval.
- Trojans: Trojans do not reproduce themselves by harming several records or devices, as opposed to viruses. Alternatively, a Trojan seems to be the sentry horse that uses other malicious software ( malware) to conceal his sinister purpose.
- Spyware: Spyware is an appropriate threshold of viruses’ ability to track behavior on a computer silently and to submit those findings to a gossiper. The information could be used to monitor your online activities, and this can be marketed to companies. Spyware could also be used to access personal data, including bank credit card details, which would lead to fraudsters.
- SQL injection (SQLi) is a type of code injection where injecting Malicious expressions can be performed. Such claims guide a web app backed by a computer system. Attackers may use security flaws in the attack vector to circumvent security protocols in the application. We will go about authenticating and approving a web address or web application and downloading all of the SQL database material. We can also use SQL Injection to attach, alter, and remove database information.
- Phishing: Phishing is really a cybercrime where someone acts as a real customer to trick persons into sharing sensitive information including such individually identifying information, financial and bank account details or password contacts a goal or objectives by email, telephone or text. The data can then be used to obtain major accounts, which can lead to identity fraud and loss of money.
The latest Cyber security Threats:
Some of the most recent cyber attacks that the U.S., U.K and Australian cyber organisation have reported are on.
- Dridex malware: Dridex is malware that attacks banking and financial accessibility by exploiting office software extensions to infiltrate systems. When a device is compromised, Dridex attackers are able to steal bank details as well as other sensitive details on the machine to reach a recipient’s financial information. Dridex bank virus was initially distributed through the use of a spam program in late 2014 which produced more than 15,000 emails per day. The attackers primarily concentrated on devices operating in the UK.
How to secure data from Cyber security attacks?
- Upgrade your operating system and software: This ensures you’ll benefit from the new security patches.
- Using anti-virus software: Security solutions such as Kaspersky Complete Protection identify and delete viruses. Keep the apps configured to the best security standard.
- Using solid passwords: Make sure the passwords aren’t easy to discover. Don’t open unidentified senders’ email attachments
- Do not click on the link through unknown sources or unknown sites in emails: it is a common method of transmitting viruses.
- Consider utilizing untreated external wireless devices: unclassified networks make you open to man-in-the-middle attacks.