6G technology
What is 6G technology (The technology of the upcoming future)?
6G technology is expected to incorporate 5G into regional satellite service networks. 6G Innovation and Quick Internet Access are considered inexpensive. It offers a high throughput and high-speed internet speed for air-access via wireless mobile smartphones with bandwidth ranges of up to 11 Gbps while traveling far away. 6-G wireless monitoring systems are required to progressively utilize different wavelengths to determine the absorption and change the frequencies appropriately. It is possible because molecules produce and consume infrared waves at specific wavelengths, and the rates of absorption and scattering for just about any given material are similar. 6G technology would have significant consequences for community security and vital asset security approaches in industry and government
The speed of 6G.
This is going to be like 5G, and more so. Still higher speeds, much-reduced cost, and bandwidth quantities. Scientists are thinking regarding 6-G moving beyond a “wired” network, with appliances operating as routers not under control by a single network provider, utilizing a network structure. Once all links together using 5G, 6G would set such smart devices apart, since higher data rates and lower latency enable immediate device-to-device communication. Last Feb US president trump’s tweet “I need 5-G, and maybe 6G technology in the US as quickly as possible” was expected to draw attention. This is not very popular for US Presidents to make public demands for mobile communications to grow more rapidly. Trump’s tub-thump continued: “6G technology is much more efficient, quicker, and smarter than the current norm.” Using the word ‘is’ attracted the most frustration from the technically educated Twitterati, since 6G, as a concrete technology, is not. There are a few fundamental problems beyond all 5-G that need to be tackled are higher network efficiency, higher bandwidth rate, lower bandwidth, and improved service quality (QoS) relative to 5G network.
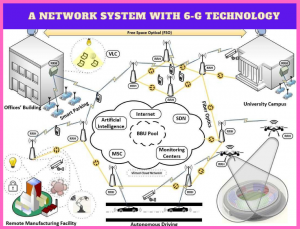
Figure 1. A network system with 6G technology
Companies that are working on 6G.
Unlike 5-G, several large corporations and governments will be focusing on 6-G programs, and some are even debating projects. Japan unveiled its 6-G initiative just recently, preceding a media briefing in January 2020 in which it declared its plan to pursue initiatives to standardize and research challenges. The above mentioned NTTDoCoMo study depicts its most thrilling picture of what 6-G could yet offer. A 6-G Flagship project has been launched by the University of Oulu, Finland, collaborating with educational institutions and corporations around the world Both companies concentrate on developing the potential network architecture and implementing innovative 6-G technology innovations, such as augmented reality interactions and essential communications with a quick response. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States agreed to open the TeraHertz (THz) spectrum for 6G and proposed using blockchain to allow for scalable and competitive spectrum sharing. While 6G’s key function of satellite connectivity is to create interconnected space-to-air-ground networks to have complete coverage around the world[5]. South Korea is aggressively studying THz connectivity and the network’s “space-air-ground”, comparable to the United States.
The technology that the 6G speedy network will adopt.
Mobile Enterprise or Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) can be used as 5-G moves to 6G. This is a communications protocol whereby intense data is being processed in close proximity to individuals on server-cum-base stations, but most of the latest results, including such AI and issue modeling, actually occurs on mobile devices or IoT. A main air chamber for the 2030 smart knowledge society, 6-G networks are expected to offer superior performance to 5-G and fulfill evolving technologies and applications. All through this post, we describe our dream of what will be 6-G and explain inter-terabyte per second (Tb / s) and sophisticated 6-G networks implementation possibilities and specifications. An essential factor for 6G is a desire to implement edge technology to maintain high performance and minimum bandwidth for ultra-reliable, reduced bandwidth communications solutions, as also the desire to enable machine-to-machine connectivity in the internet of things (IoT). In addition, a close link between potential 6-G technologies and high-performance computing (HPC) has been established. Although some of the data on the IoT platform will be managed by edge computing resources, most of it will involve highly hierarchical HPC services to analyze.
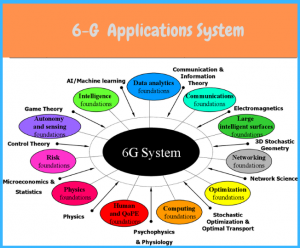
Figure 2. 6-G applications system
The advantages of 6G technology over 5G technology.
6-G Velocities are required to reach 1 terabyte per second (Tbps). This capability and bandwidth rate would be unparalleled but will improve the efficiency of 5-G networks together with widening the capability spectrum to accommodate progressively fresh and novel networks in the domains of wireless perception, processing, and imaging. The longer wavelengths of 6-G would allow for very much faster-sampling speeds, in addition to dramatically improved efficiency. It is expected that the application of sub-mmWave (e.g. wavelengths below one nanometer) and the use of broadband applications to assess relative electrical diffusion levels can contribute to possibly important developments in wireless sensing.
Emphasis on spatial bandwidth increased by the Scientist:
Some researchers have referred to increased incorporation of satellite communications to boost the bandwidth as well as the 6-G system ‘s spatial acuity. Nonetheless, it would appear that moving forward, evaluating performance in terms of ability to produce samples per second per m3, rather than only bits per second, was becoming important. Of course, 5-G already exists in the spread spectrum angle (if you’re going to forgive the play on words) of the issue with massive technology enabling high precision lasers to be guided to specific customers. Yet the industry has yet to get to terms on how to quantify the true value of this technology, in our personal experience, which is, of course, calculated in dollars rather than dB, leaving other fantastic inventions still waiting for proper encouragement for development. As this all worked out, hopefully, 6-G will come and there’ll be a new drive for technology that will increase the spatial complexity of b / s as well as a healthy respect for its importance. While there are some attempts to boost modulation Technique with 6-G as their goal beyond the existing state of the art. Nonetheless, we expect that much remains to be achieved in expanding spatial bandwidth far beyond existing MIMO products, which are also failing to make a significant difference in itself.